3D printing is growing in popularity year on year. It is used in small businesses as well as multinational corporations. If you are not realising the potential of 3D printing in your business then read the article below and see real life examples that are used every day.
3D printing is a technique that creates a spatial object. First developed in 1984 by American Charles Hull, it was an incremental – stereolithographic (SLA) technology. This builds the model layer by layer. There are more than a dozen 3D printing methods.The method should be selected depending on the model, the material from which the model is to be made, the complexity of the model, or the lead time. The most popular methods of 3D printing – FDM (incremental method), SLS (joining particles of material (powder) by laser beam), SLA (using photopolymer resin), DMLS (laser welding of metals and their alloys on a small scale (micro)), PolyJet (resin, for very accurate models).
With a 3D printer, you can print components in various shapes and formats from a wide variety of materials for a variety of applications, such as industrial applications (prototyping, metrology, small batch production of finished products, maintenance).
One of the most repeated elements of 3D printing application in any industry. Creating prototypes is very easy, all you need is a properly prepared STL design and you can quickly get several versions of it made from different materials. Then test which one best fits the application.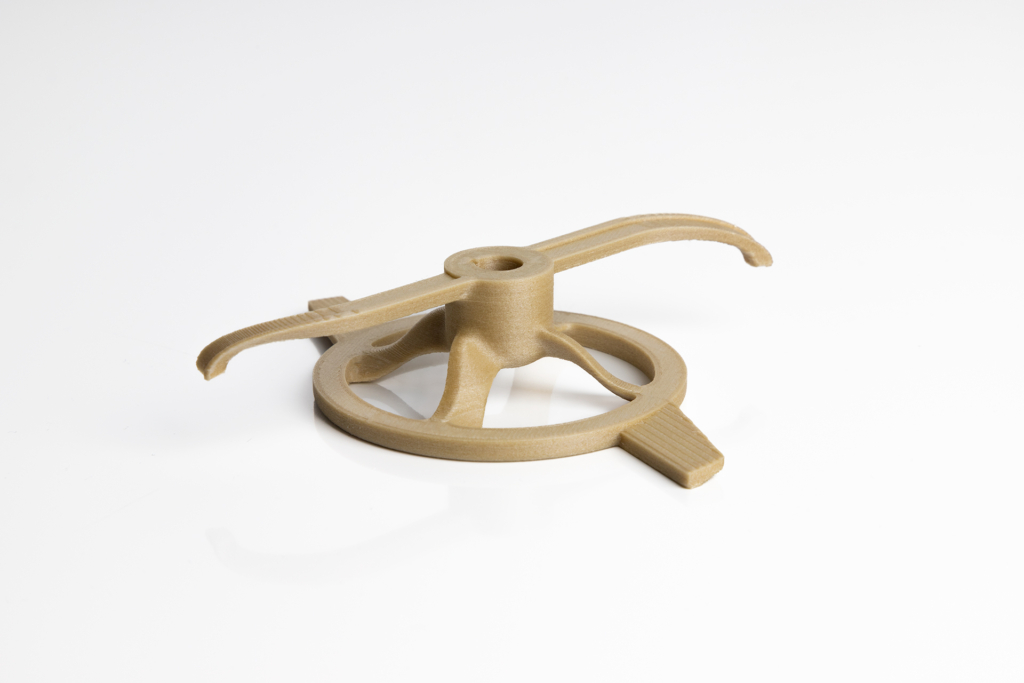 
Photo 1. Printout of a chemical stirrer blade made on a VSHAPER 500 Pro printer, in PEEK+GF material
By using the right materials, e.g. PEEK with carbon fibre, which has a high mechanical strength, we can create very durable components, sometimes even replacing metal components. Nowadays, powder metal printing has also begun to be used, which makes it possible to obtain shapes that are not possible with other methods. However, research is underway to make this method safe, as currently the fumes emitted when printing with this method can be hazardous to humans. This printing method is more expensive than conventional methods.
Depending on the printer’s working area, we can print larger or smaller models. In addition, for larger models, post-printing processing is important, which allows several parts to be joined together to produce an even larger part, such as a propeller.
3D printing can be used in any industry. If it is not used in any industry, it only means that no one has yet figured out how to use it, not because it is not possible. Sooner or later, 3D printing will find its way into every industry.
3 D printing in medicine is developing at an incredible pace. Therefore, patients are being offered new solutions that can improve their lives. The print is being used to create prostheses, orthoses, a stabilising element in cancer treatment, to print medicines. Research is also underway to print organs or even skin, prints made to simulate procedures (e.g. complex surgery). Some solutions sound unbelievable, but this will probably be the norm for us in a few years’ time.
3D printing in orthopaedics is intended, among other things, for amputees in the lower leg. A key component of any prosthesis is the prosthesis funnel, which is designed using 3D scanning and computer-aided modelling. The production of the prosthetic funnel is achieved using innovative 3D printing technology. This allows us to create a perfectly fitting prosthesis that provides comfort and functionality for the patient.
3D printing in medicine offers enormous possibilities. Thanks to a wide range of materials, we are able to prepare the test funnel from materials such as PET-G, PP, ABS, as well as the final funnel from PA-6, PA-12. This significantly improves the duration of prosthesis production and patient comfort. Preparation time can even be reduced from a month to a few days.
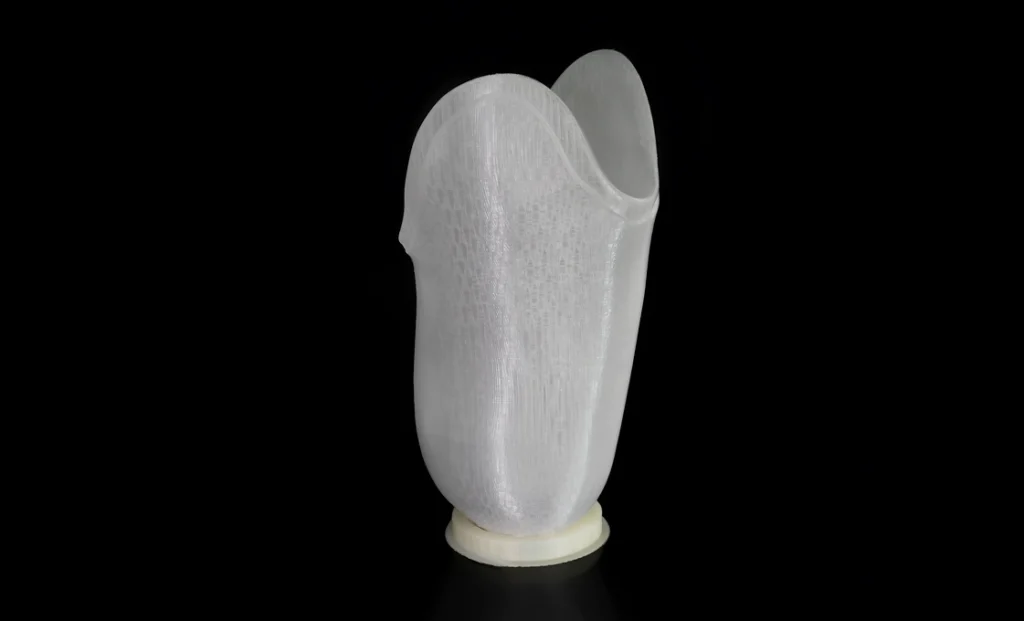

Images 2. A femoral prosthetic funnel made on a VSHAPER 500 PRO printer for an orthopaedic equipment company. The design was based on a 3D scan. Material: PET-G
In addition to prostheses, in orthopaedics models of the hand, skull, leg are created to create customised orthoses , a protective element after surgery, for example. In standard processes, models are created using plaster, which makes the process longer (takes about 2 weeks). With 3D printing, the process can be shortened to 1 day.
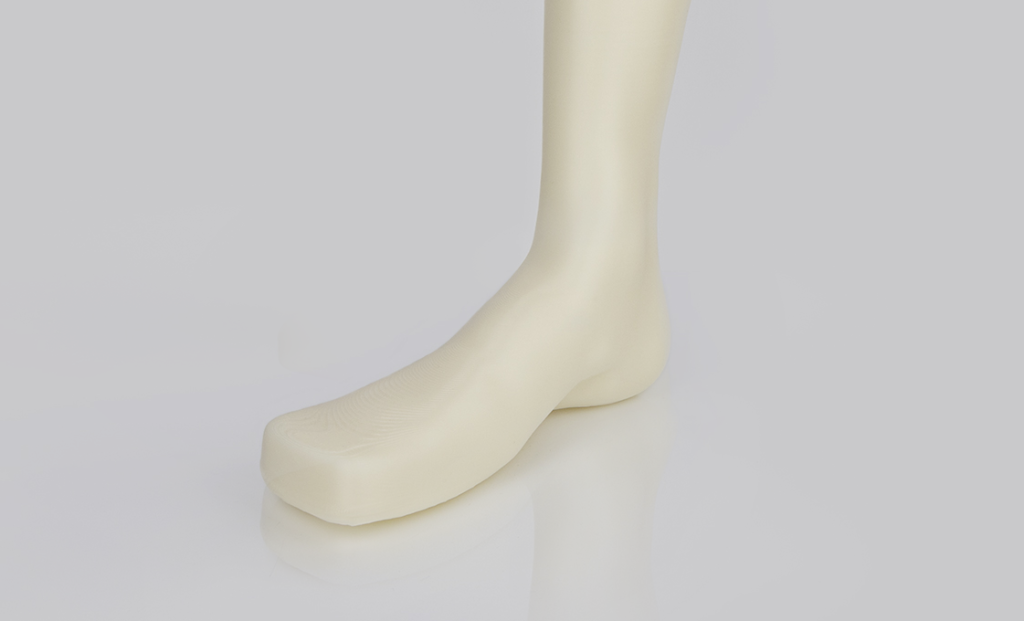
Photo 3. A leg model created from a scan, to create personalised orthoses that improve quality of life. Made of ABS material, due to the price of the material and the degree of hardness.
3D printing is also used in radiotherapy to create compensators (boluses), whose radiation attenuation coefficient is similar to that of water. Their use allows for a more homogeneous dose distribution and an increase in radiation to the tumour site. They are most often made of PLA or ABS materials. To prepare the bolus, a shape is drawn on the patient and then an image is obtained using tomography, which is processed into a printable model in STL extension. The greatest difficulty in creating a bolus is to create a solid piece of the model, with a homogeneous filling. It is important to use appropriate programming with layer grouping for this.
Aerospace is another very important industry in which 3D printing is increasingly used. According to manufacturers, Boeing can save several million dollars on aircraft production using 3D printing. In aviation, 3D printing is used in the creation of prototypes, but also increasingly in the creation of final components. Among others, fuel nozzles for aircraft are printed. Often 3D printing is used in the manufacturing processes of aircraft components – maintenance, tooling production and others. Engines prepared with 3D printing achieve higher efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. In addition to components relating to the construction of aircraft interiors, 3D printing is used to print components in the aircraft cabin, where passengers are, e.g. tables, seat components. Thanks to a wide range of filaments, durable as well as lightweight materials are chosen, which is particularly important for aircraft.
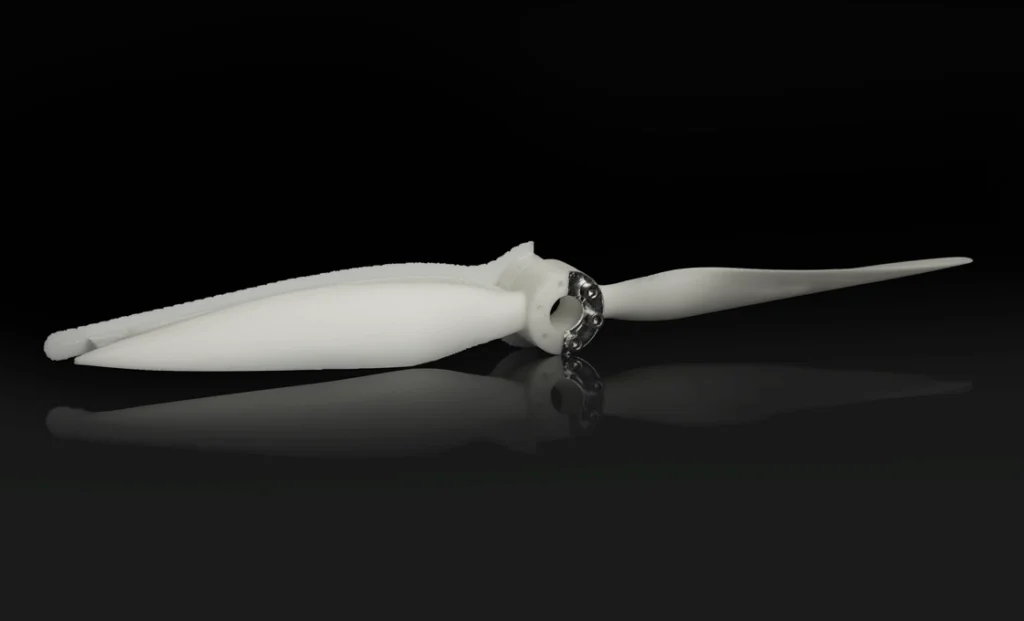

Photo 4. 3D printed propeller model, material: ABS
In industry, as in other industries, there is a particular focus on prototyping, small batch production. The wide range of materials makes it possible to test and find the ideal material. In addition, the use of 3D printing reduces production time by up to several tens of per cent and leads to lower production costs. Another key advantage is its flexibility and independence. Parts can be printed at a lower point in time, without waiting for other suppliers. Even complex shapes can be printed.
In addition to the production of components for larger equipment, e.g. in automotive, mechanical engineering, etc., 3D printing helps to keep the production line in good condition by printing wear parts or creating a new production line. The use of 3D printing in small batch production is much cheaper and faster, which is why more and more companies are opting for it.
Thanks to our advanced prototyping capabilities (SolidWorks) and incremental FDM technology, we have reduced machine running costs by 40% and created an innovative way of remanufacturing industrial machine components to ensure continuous supply. The model was made from PEEK filament, which is biocompatible, necessary in this case due to the use of the printed model in contact with food. Printed on the VSHAPER 500 PRO printer.
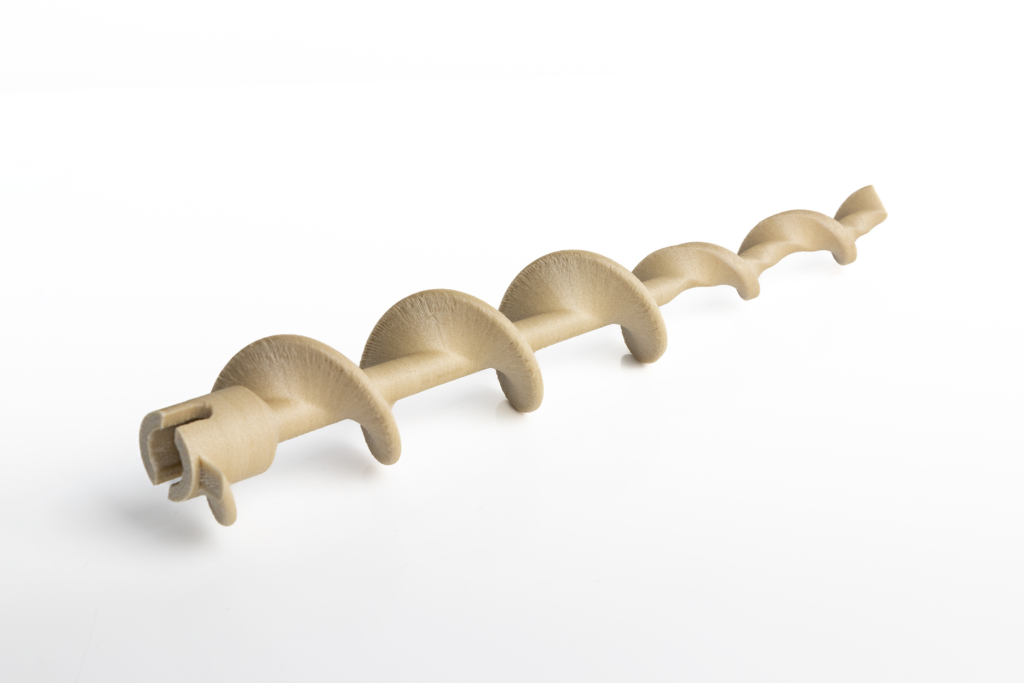

Photo 5. Feeder model printed on VSHAPER 500 Pro, material: PEEK+GF
A nozzle used to apply a thin layer of glue used on an automotive production line. Originally, the customer used a metal nozzle, but gluing was done at a high temperature and also the adhesive was highly corrosive, so the metal surface degraded. By using PEEK filament, the problem was eliminated, production costs were reduced and rapid wear of the component was prevented.
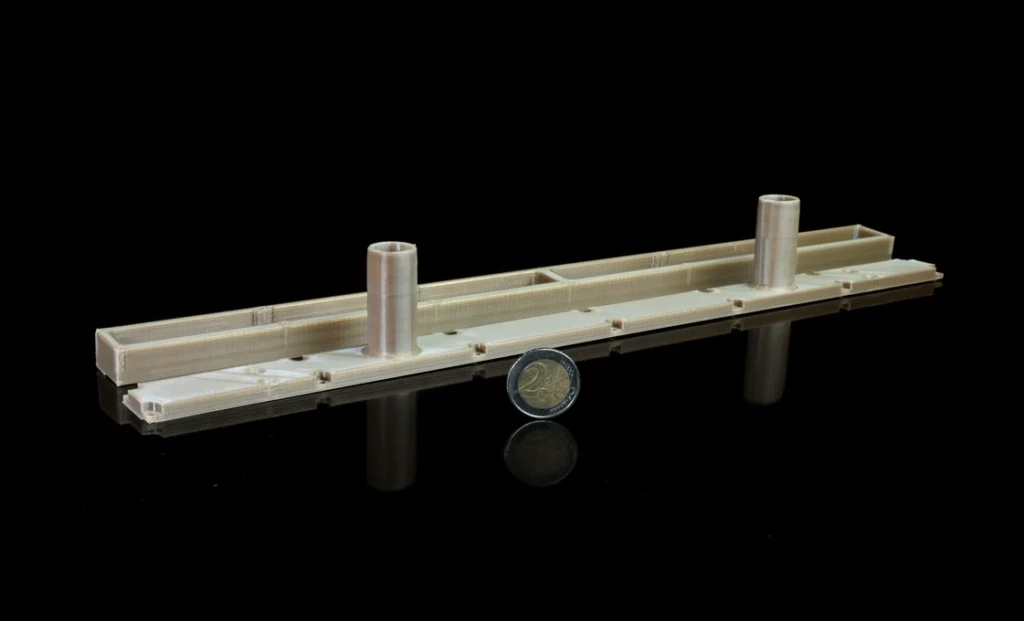
Photo 6. Nozzle for glue application, material: PEEK
Robot gripper, building block of a robot – an improvement on automated production lines. Responsive take-up and refitting of automated robots in Think 4.0. Thanks to the use of 3D printing technology, the production of grippers is much cheaper, faster and more efficient. In addition, gripper shapes unattainable with other production methods can be achieved.
In the automotive industry, 3D printing is slowly replacing CNC machines, which are more difficult to operate and the creation process is longer. Training employees to operate CNC machines is also more difficult. A problem that has arisen in this industry that can be solved by 3D printers is a broken/delayed supply chain due to war/pandemics.
The important thing at this point is to depend on other suppliers and thus streamline the process and reduce production costs. . example is a multinational automotive brand that has implemented this solution and can soon enjoy a return on investment. 3D printing was used to create positioning and assembly tools and a cowl. The technology was also used to join parts printed using 3D printing and a CNC machine.
The choice of printer depends primarily on the complexity of the detail you want to print and the material it is to be made of. Then we can choose the printing method we want to use. The choice of printing method affects the turnaround time. It is also necessary to determine what working area is needed and the temperature of the feeder and inside the chamber.
Today, we have a very wide choice of filaments on the market, which are used in various fields. There are some industries that require filaments certified for use in the human body, such as PEEK. Before selecting a filament, it is worth considering which properties we care most about.
If, for the time being, you are not sure whether a printer will work in your industry, you can use a 3D printing service. This will get your model printed in no time and give you an idea of the speed, flexibility and performance of a 3D printer.
What to look for when choosing a 3D printing service?